the space. An old hat at this young technology, he has been making
waves as the CTO of Ripple labs. In a recent effort he has set his
sights on smart contracts technology. The designs and implementation he
and his team have come up with are interesting, to say the least.
and contracts can interact with any service that accepts
cryptographically signed commands. The paper also includes an
implementation of smart oracles, called Codius (based on the Latin “ius” meaning “law”).
business, and law that have the potential to usher in a wave of
innovation and serve as a building block for a next chapter of the
internet.
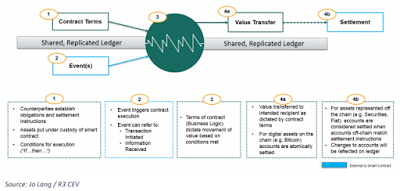
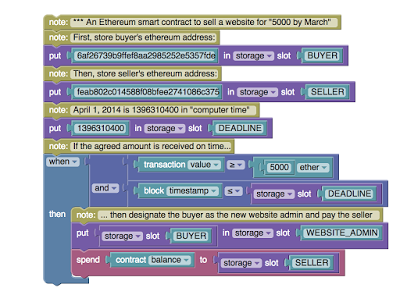
and outcomes of a legal agreement into a computer program. Rather than
rely on another party to enforce the terms of the arrangement, the
obligations of a smart contract are settled automatically and
autonomously through the execution of its code.
provide an important building block for smart contracts by allowing the
transfer of digital assets with a cryptographic signature. The benefits
of using smart contracts instead of traditional contracts are increased
speed, efficiency, and trust that the contract will be executed exactly
as agreed.
| Uatu, The Watcher |
inform contracts about the state of the outside world. Bitcoin contracts
rely on “oracles”
to attest to facts from the outside world by introducing signatures
into the network if and only if specific conditions are met.
whether or not someone had died. Such a system typically requires the
smart contract code to be executed on the consensus network itself. But
encoding advanced logic and executing untrusted code is complicated to
integrate. Until now, this has been one of the primary obstacles for
creating a viable smart contract system.
the untrusted code execution in the oracles’ hands. Smart oracles, then,
are trusted or semi-trusted entities that can both provide information
about the outside world and execute the code to which the contracting
parties agreed.
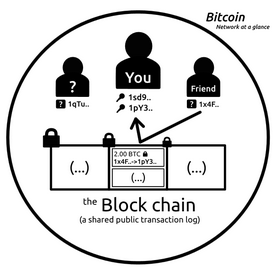
databases and other services that track and transfer asset ownership,
smart contracts can be achieved without increasing the complexity of
existing consensus networks like Bitcoin and Ripple.
 |
| Algolon, The Observer |
using smart oracles can interact with multiple networks at once as well
as virtually any type of online service. This means that a single smart
contract could interact with Bitcoin and Ripple, web-based services
like PayPal, Google, Ebay, etc. or even other Internet protocols, such
as SSH, LDAP, SMTP and XMPP.
developers with a robust and familiar platform to build smart contracts
and hit the ground running. Because Codius uses Google’s Native Client to sandbox untrusted code, developers can write contracts in any programming language.
developers, entrepreneurs, and enterprising legal and financial
professionals. Agreements that previously required lengthy legal
contracts can be translated into code and run automatically by smart
oracles.
fairer, more affordable and more efficient legal system and smart
oracles are one of the simplest ways to realize that dream. Potential
use cases include bridges between value networks, escrow, cryptocurrency
wallet controls, auctions for digital assets, derivatives, debt and
equity, smart property and voting.