(
Sole24Ore) “A contract is an agreement”, this was the mandatory phrase for starting a private law exam test after which we would discuss the conditions for its validity. Today, university memories are coming back as contracts are revised in technological form; indeed they’re called
Smart Contracts. This brilliant intuition came from
Nick Szabo who proposed them in 1994, even before Bitcoin and the diffusion of the Internet.
“Smart Contracts are computer protocols that facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract, or that obviate the need for a contractual clause. Smart contracts aim to provide security superior to traditional contract law and to reduce other transaction costs associated with contracting.”
The words in bold about automatic performance of the clauses is a source of opportunities and risks, questions and doubts. One thing is certain: A Smart Contract isn’t a contract, but only the part related to agreements performance.
Until now, when one of the contracting parties feels the other party didn’t respect a clause of the contract then a third party need to be called in order to settle the conflict. This neutral authority has always been a human one. Now, we rely increasingly on technology to facilitate relationships between humans, even if this could seem an oxymoron. Maths (or should we say cryptography) intends regulating any operation between each one of us, close or far, a known or unknown stakeholder.
How do technology and economy meet at this point?
If a contract represents the formalization of an agreement, how can we make it secure between parties that remotely agree and maybe don’t even know each other? The answer is
Smart Contracts based on
Blockchain technology.
The contract then becomes an instructions set. If it can be codified, it can also be “computed”, i.e. if the conditions are satisfied, it ensures that performance is automatic.
It sounds like a futuristic scenario, but in reality the Internet of Things (
IoT) includes this form of contracts for new services. All is fine, in the end “equal justice for all”, not only for those who possess the power. Eliminating all excess of human discretion which leads to long and inconclusive civil lawsuits is actually one step forward.
But in which direction?
If we choose the one that leads to no human discretion at all, the risk may be even greater. These systems are fascinating, they open up incredible scenarios, but they also are autonomous and immutable. This isn’t good, machines must remain instruments. They mustn’t have the last word. Otherwise this will be the first step on a slope in which decision power is given to machines. Instead, we would like machines that assist us in the decision-making process. We must leverage them but not be ruled by them. The variability of emotions remains a human factor that we shouldn’t give up.
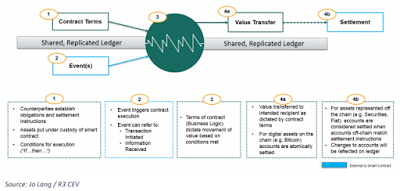
The third party, not human, to which we entrust the performance of contract can’t always be mathematics. We hope for a coexistence with the practitioners: the new generation lawyer will have to know how to write a Smart Contract, for
example translating the clauses into computer code as shown in the figure.
All this to emphasize the fact that Smart Contracts should be used to control the performance, and never to judge. New technologies require for behavioral models to adapt. . We must use them according to their usefulness, without extremisms. We will use these instruments but wisely, because we don’t live in a deterministic world. Not yet.
Open your free digital wallet here to store your cryptocurrencies in a safe place.