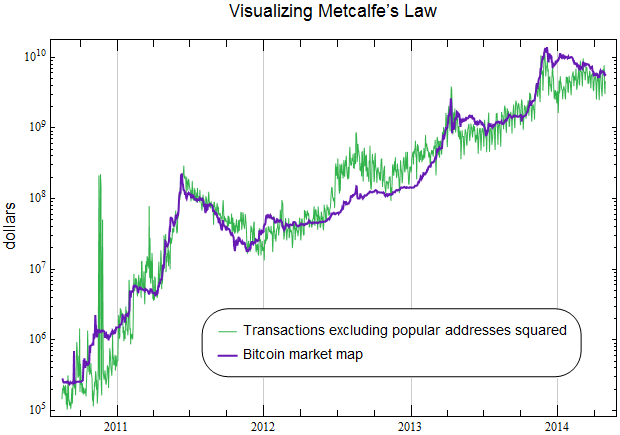
(HarvardBusinessReview) Digital currencies like Bitcoin have captured the attention of
the media, entrepreneurs, and regulators. The coverage has described
exchange meltdowns, price volatility, and government crackdowns.
However, the focus on Bitcoin as a currency may distract businesses and
governments from its disruptive impact: as a technology.
Bitcoin is more than just a new way to make purchases. It is a
protocol for exchanging value over the internet without an intermediary.
Bitcoin is based on a public ledger system, known as the blockchain,
which uses cryptography to validate transactions. Bitcoin users gain
access to their balance through a password known as a private key. As a
result, Bitcoin is peer-to-peer and open, yet secure and nearly
frictionless. Much has been written about the payment applications of
Bitcoin, including remittances, micropayments, and donations.
However, Bitcoin could disrupt other systems that rely on
intermediaries with a similarly open, peer-to-peer system, including
property, contracts, and identity management.
Anywhere a transaction between two parties has traditionally required
third party validation, Bitcoin may be applicable. Consider these three
common actions:
Transfer of property. The Bitcoin protocol could
simplify complex asset transfers, revolutionizing the services that
support this industry. Currently, the transfer of large assets requires
significant time and resources. For example, in order to purchase a car
from an individual seller, one has to engage a third party to transfer
the title. Additionally, one has to use services like Carfax to learn
about the car’s accident and inspection history. And who doesn’t like to
spend a Saturday at the DMV updating a car registration?
The blockchain could change all of this. Bitcoins can be qualified in
such a way that they represent real-world assets. Bitcoin entrepreneurs
at companies like Colored Coin
are already working on ways to use small portions of Bitcoin to denote
physical property. A fraction of a Bitcoin would publicly identify who
currently owns that property, and could include a record of both past
ownership and other history about the property. When purchasing the car,
one would be able to verify all accidents and inspections over the
blockchain and transfer the title on site. Similarly, real estate and
financial instrument transactions could all be executed over Bitcoin.
This could soon create efficiencies and reduce friction by allowing
individuals to directly transfer property without the use of a broker,
lawyer, or notary to sign-off on the transfer.
Execution of contracts. Bitcoin could similarly be
used to structure contracts, bringing new efficiency and transparency.
Contracts are typically developed by lawyers on a case-by-case basis
with significant time and resources devoted to negotiation, development,
and enforcement. Additionally, markets based on contracts, including
certain financial derivatives markets, lack transparency, which
complicates regulation.
Traditional contracts could be replaced by code, executing themselves
when a triggering event occurs. In a simple example, a financial
instrument, like an option, could be developed and executed over the
blockchain. In addition to reducing legal fees, this could bring new
transparency to financial markets, as regulators could use the public
ledger to understand the market without forcing individual actors to
reveal their specific positions. It is possible that new
crypto-currencies will emerge to serve these niche purposes.
New ventures, like Ethereum, are creating these capabilities today. Ethereum is developing a network to serve as both the registry and escrow to execute the conditions of a contract automatically through checkable rules.
Identity management. Bitcoin’s cryptography could also transform identity management. Much of identity management, including passports, still operates on a paper-based system.
These documents are frequently forged and stolen. Interpol’s database
currently lists 39 million stolen travel documents. Instead of carrying
paper documents, what if there was a way to create a unique, verifiable
key that was impossible to forge?
A cryptographic network similar to but separate from Bitcoin could be
used to verify individuals’ identities and monitor movement across
borders. When a person travels through a checkpoint at a border
crossing, instead of showing and scanning a paper passport, she could
present her private Bitcoin key. A network privately maintained by the
government could verify the key and register the entry into the ledger.
This system, based on cryptography instead of paper documents, would
simultaneously increase mobility and security. If Bitcoin can be used
for travel documents, it could also be used for other forms of identity
management like social security numbers, tax identification numbers, or
even driver’s licenses.
Property, contracts, and identity management are only a few examples
of how a peer-to-peer, open, and frictionless system could change how we
conduct business in the future. In order to achieve this wider
adoption, Bitcoin will need to address significant questions around
trust, ease of use, and operability. However, the Bitcoin community has
shown remarkable adaptability and is already working to mitigate these
problems. In the next decade, we can expect significant innovation
around the Bitcoin network. Much of that will revolve around payments,
particularly early on. The real value, though, lies beyond.